Additional Masculinizing Bottom Surgery Procedures
Medically reviewed by Ellie Zara Ley, MD on October 3, 2024.
Many patients who undergo a phalloplasty or metoidioplasty seek out additional procedures to help them achieve their surgical goals. Below we describe the supplementary procedures we can offer a patient as a part of their bottom surgery journey. We have grouped these procedures into the following three categories: (1) removal of the natal genital or reproductive organs, (2) alteration of appearance (of the tissue created from a phalloplasty) and (3) alteration of function (to facilitate erections or to enable urinating while standing):
- Removing natal genital or reproductive organs:
- A vaginectomy is the removal of the vaginal canal.
- A hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus, which is a necessary predecessor to having a vaginectomy.
- An oophorectomy is the removal of one or both ovaries. We do not require this procedure for any of our patients.
- Altering appearance:
- A mons resection and panniculectomy involve liposuction and excision of excess skin, respectively, to help give the penis a more forward, apparent position on the body.
- The split thickness grafts and full thickness skin grafts are used to cover up scars on the forearm that come from a phalloplasty and/or urinary lengthening procedure.
- A glansplasty creates a glans or a “penis head” to the end of a penis created from a phalloplasty
- A scrotoplasty and testicular implants involve the creation of a scrotum, their expansion and eventual insertion of silicone implants to create the appearance of testicles.
- Altering function:
- A urethral lengthening involves extending the urethra to the tip of the penis so that someone can easily urinate while standing.
- An erectile device can be inserted into the penis created from a phalloplasty to facilitate penetrative sex.
Removing natal genital or reproductive organs:
Vaginectomy
- What is a vaginectomy?
- A vaginectomy is the removal of the vaginal canal. This procedure involves the removal of the mucosal lining and closure of the canal’s opening. In order to undergo this procedure, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) must be performed beforehand. This procedure does not require that a patient have their ovaries removed.
- Why would a patient get a vaginectomy?
- Most of our patients seek out a vaginectomy as a part of their surgical gender affirmation plan.
- Patients who would like to get a urethral lengthening as a part of their metoidioplasty or phalloplasty must get a vaginectomy. Urethral lengthening gives patients the ability to urinate while standing since it allows urine to exit from the tip of the penis. There is a high risk of complications with urethral lengthening if a patient does not have a vaginectomy. While some surgeons do perform urethral lengthening without requiring a vaginectomy, we feel as though it is best for our patients to not offer this option due to the significantly increased complication risk.
- What is the recovery from a vaginectomy like?
- Many patients who undergo a vaginectomy experience blood drainage from the wound site for a few weeks after the operation. Bleeding should subside substantially as time goes on.
- Many patients experience pain and discomfort from sitting down that should subside over the course of the first few weeks or months after surgery.
- More specific care instructions will be given to you by your surgical care team.
Hysterectomy and/or oophorectomy
- What is a hysterectomy? What is an oophorectomy?
- A hysterectomy is a removal of the uterus. This procedure often involves a removal of the fallopian tubes and can also involve a removal of the cervix and/or vaginal canal.
- An oophorectomy is the removal of one or both ovaries.
- Why would a patient get these procedures?
- Medical complications linked with the uterus and/or its surrounding organs are one of the reasons that a patient may want to remove them.
- If a patient is interested in a vaginectomy as a part of their gender affirmation surgical plan, they will need to arrange a hysterectomy at least 8-12 weeks prior.
- Removing one or both ovaries is not a requirement to undergo other gender affirming bottom surgery procedures. Patients may choose to remove one or more of their ovaries due to medical complications or gender affirmation. Since an oophorectomy is essentially a sterilization procedure, we recommend that patients learn about their reproductive health and fertility preservation options beforehand.
- What is the recovery from these procedures like?
- Generally speaking, patients are given 4-6 weeks to recover from a hysterectomy. Some patients may return to work as soon as 2 weeks post-op. The most common experience from recovery is pain and discomfort exacerbated by sitting down, which can persist several weeks after surgery.
- More specific care instructions will be given to you by your surgical care team. Please note that the GCC does not offer hysterectomy or oophorectomy procedures at this time.
Additional bottom surgeries to alter appearance:
Mons resection and/or panniculectomy
- What is a mons resection? What is a panniculectomy?
- A mons resection removes the fat and tissue over the pubic area. A mons resection generally leaves a thin, horizontal scar just above the pubic area.
- A panniculectomy removes stretched out or overhanging skin and fat from the abdomen. This is often done for people who have excess skin, often because of a large amount of weight loss.
- Why would a patient get these procedures?
- A mon resection can help to further elevate the position of the penis on the front of the body.. A mon resection cannot be done at the same time as any other bottom procedures. It is required to wait a minimum of 3 months in between a mons resection and additional bottom surgeries.
- A panniculectomy may need to be done prior to a phalloplasty or metoidioplasty to prepare the pubic area. Your individual surgical plan can be reviewed during your consultation. .
Scrotoplasty and Silicone testicular implants
- What is a scrotoplasty? How can silicone testicular implants be placed into the new scrotum?
- During a scrotoplasty, the surgeon creates a scrotum using the tissue from the labia majora. A scrotoplasty can be performed during the initial metoidioplasty or later on for a phalloplasty surgery, with the option of inserting testicular implants once the area has fully healed.
- Testicular implants are generally silicone prosthetics which are placed within the scrotum to give it a fuller appearance and feel. Some people do not have adequate space in their scrotum to allow for safe insertion of testicular implants. In this case, tissue expanders can be placed prior to testicular implant placement. Tissue expanders are empty implants which are slowly filled with saline over time to help stretch out the skin.
- Why would a patient get a scrotoplasty and/or testicular implants?
- For many patients, their gender affirming surgical goals include having a scrotum with the appearance and firmness of testicles.
- What is the recovery from these procedures like?
- Scrotal tissue expanders are generally inserted 3-4 months after the scrotum is constructed. With tissue expanders, you would inject saline into a port leading from the outside of your body into the expanders 2-3 times per week.. Tissue expanders generally stay in for about 4-5 months. At this point, silicone testicular implants will be inserted into the scrotum.
- We advise patients to be mindful of making harsh movements that can stretch the groin area as this can cause wound opening, which can prolong the overall healing process. We do not suture reopened wounds from bottom surgery due to infection risk. Thankfully, simple wound care should resolve the issue over time.
- More specific care instructions will be given to you by your surgical care team.
Glansplasty
- What is glansplasty?
- Glansplasty shapes the tip of the penis to give it a defined coronal ridge, which gives it the appearance of a circumcised penis.
- Why would a patient get a glansplasty?
- Glansplasty is a procedure that is used to alter the appearance, not the sensation, of the penis. A glansplasty cannot give a phalloplasty patient concentrated sensation in the “head” of their penis.
- What is the recovery from a glansplasty like?
- It takes about three weeks for incisions to heal and six weeks for inflammation to subside enough to be able to see what the final surgical results should look like. Patients should not engage in sexual activity with their penis until it has fully healed.
Split thickness and full thickness skin graft for phalloplasty scars
- What is a split/full-thickness skin graft? Why would someone get it?
- Patients who get a radial forearm (RFF) phalloplasty are left with a large scar on their forearm from the skin graft that was taken to construct their penis. Depending on the thickness of the graft, a split or full-thickness skin graft will be placed over the forearm 2-4 weeks after the initial procedure.
- A split or full thickness graft takes a skin from the thigh and uses it to cover the donor site––generally the forearm where the flap was taken from.
- What is recovery like?
- The place on the body where the graft is taken from will appear to be similar to a “road rash” injury for a few weeks post-op.
- A skin graft may be a different color or texture than the untouched skin around it. Often, the skin will eventually fade back to your normal skin color, but this does not happen for everyone and depends on a variety of factors.
- Healing a skin graft depends on your personal scar care, exposure to the suns, as well as your own genetic predisposition to healing.
Additional bottom surgeries to alter function:
Urethral lengthening
-
- What is urethral lengthening?
- The urethral lengthening procedure lengthens the urethra through the penis, which is what urine travels through to exit your body. This will allow you to urinate out of the tip of your penis. For a metoidioplasty, the new urethra is created using labia minora tissue. For a phalloplasty, the new urethra is created using the labia minora tissue in conjunction with forearm tissue. For a phalloplasty procedure, hair must be permanently removed from the forearm or thigh donor site, through electrolysis, to ensure that hair does not grow inside of the urethra.
- Why would a patient get urethral lengthening?
- The primary reason patients get urethral lengthening is to gain the ability to pee standing up.
- What is needed to prepare for this procedure?
- Patients that would like to undergo a primary urethral lengthening (PUL) for a phalloplasty that uses a skin graft from the forearm must undergo Electrolysis hair removal of the corresponding area before surgery. The zone needing permanent hair removal is marked below in orange. For more information, click here.
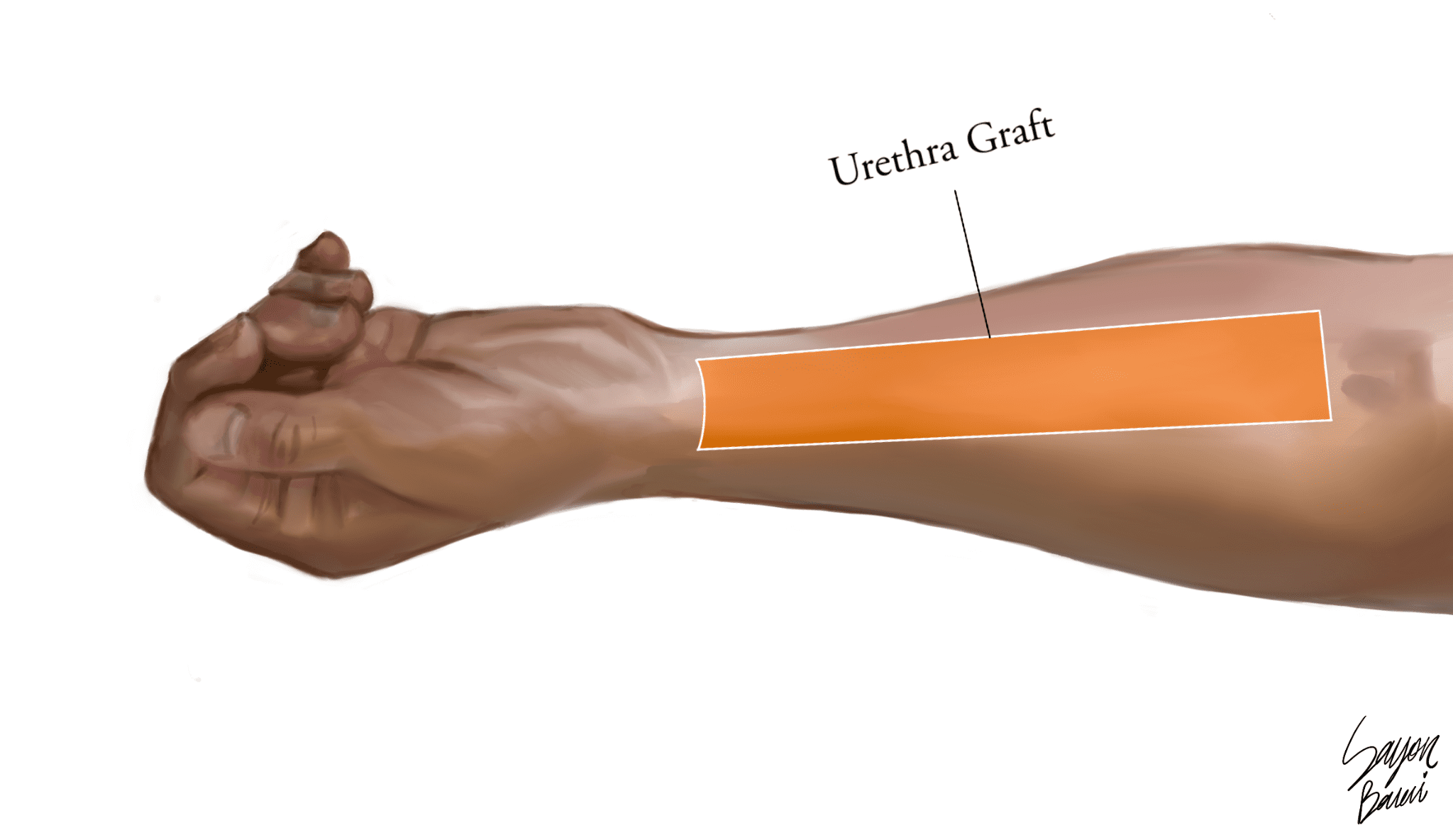
- Patients that would like to undergo a primary urethral lengthening (PUL) for a phalloplasty that uses a skin graft from the forearm must undergo Electrolysis hair removal of the corresponding area before surgery. The zone needing permanent hair removal is marked below in orange. For more information, click here.
- What is urethral lengthening?
- What is the recovery from urethral lengthening like?
- If you are getting a urethral lengthening, there are two key factors to be aware of. Firstly, you must have a vaginectomy in order to have urethral lengthening.. Secondly, you will be discharged from the hospital with two catheters. Your surgeon will discuss with you the length of time the catheter must stay in while you are recovering.
- Patients should avoid sexual activity alone or with partners until three months after surgery to allow the urinary tract to heal properly.
- More specific care instructions will be given to you by your surgical care team.
Erectile device for phalloplasty
- What is an erectile device?
- Phalloplasty patients who would like to gain the ability to have erections can have one of two erectile devices inserted into their penis 12 months after their phalloplasty has healed. Patients can opt for a semi-rigid rod or an inflatable saline pump.
- A semi-rigid rod would give the penis the same rigidity at all times and allow it to be bent into different positions.
- An inflatable saline pump is a 3-part system: a reservoir, which holds saline, a pump placed in one side of the scrotum, and then one or two cylinders inserted into the shaft of the penis. Tubing connects these three pieces. The pump in the scrotum is squeezed in order to fill the cylinder(s) with saline from the reservoir. When the pump is not in use, the cylinders are flat, and the saline remains in the reservoir. The reservoir is most often placed in the lower abdomen.
- Why would a patient get an erectile device?
- Many phalloplasty patients use external devices like a silicone erectile sleeve to allow them to have penetrative sex with their penis. Patients opt for erectile devices for a number of reasons that usually have to do with how they would like to engage in penetrative sex.
- Patients who chose the rod tend to do so because the hydraulic water pump carries a risk of malfunction and leakage that can be more difficult to repair. Patients who chose the pump tend to do so because the rod leaves the penis in a state of constant erection that makes it difficult to conceal with tight clothing.
- Your surgeon will advise you that both implants carry risks of infection and extrusion.
Request a Free Surgical Consultation Today.
All virtual and in-person consultations with our board-certified surgeons are free. Once you fill out this form, our patient care team will reach out and guide you through every step to get to surgery.




